Every single domain is part of tree and a forest.
Why multiple domains?
If you want multiple locations. There will be a main domain and based on location, there will be child domains or sub domains. If main domain is called mydomain.com, the child domains will be based on location uk.mydomain.com, jp.mydomain.com etc.
There should be trust relationship between parent and child domains to share data and resources.
Domain administrators can only control that 1 particular domain ,either parent or child, but enterprise administrators can control all domains.
If a subdomain has parent domain name it it, it means they are part of a tree.
We can have forest trust between mydomain.com and another main domain called seconddomain.com; This allow them to share resources but not schema, i.e. it we create a special type of object in 1 forest will not replicate in another forest
Used to replicate for multiple domains or domain controllers.
Active directory database is stored in a file called : NTDS.dit in your domain controller.
Active Directory have mainly 3 partitions
1 – Configuration Partition
Information about how forest is configured, will replicated forest wide on domain controllers.
2 – Schema Partition
Contains information about blue-prints of various objects created in the domain controller like groups, users etc. It does not store the object itself like username, password details of the object, it will only have the blue-print, so that it can build the object
3 – Domain Partition
This partition is unique to domain. Replicates only to DCs with in that domain only.
4 – Application/Custom Partition
Custom partition. We choose which DCs get copy of the information.
Active directory nowadays comes with some built-in custom partitions:
- ForestDNSZone Custom partition
- DomainDNSZone Custom partition
Global Catalog
Special job we can assign to domain controller, it replicates sub-set of objects in domain partition to all other domain controllers in the domain, so that domain controller can find the object in another domain controller.
Deploy And Manage Domain Controller On-Premise Steps:
1 – Name your domain controller
Go to Server Manger > Local Server
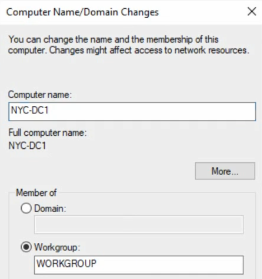
Do not restart yet
Go to Server Manger > Local Server > Ethernet > Properties
- Disable IPv6
- Go to properties of IPv4
- Set DNS server address as loop back address of the server itself, because active directory will install DNS for us.
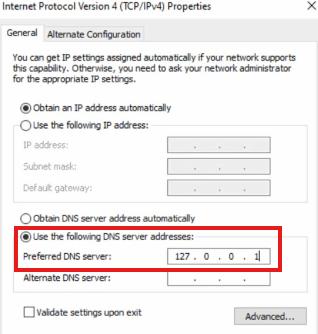
Reboot the computer
2 – Add Active Directory Domain Services Role
Go to Server Manger > Manage > Add Roles and features
Add Server Roles : Active Directory Domain Services
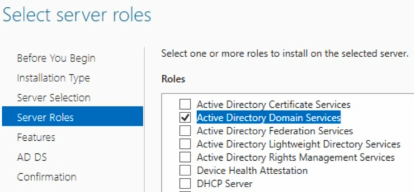
3 – Promote server as Domain Controller
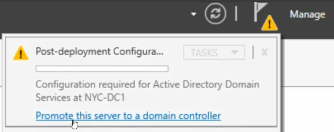
Add a new forest, since we are starting a new domain
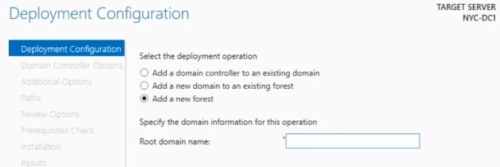
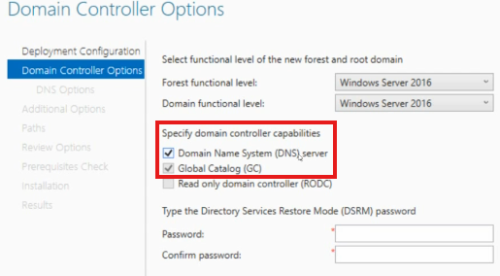
DSRM password is used to restore active directory from the backup.
After reboot check if:
DNS is installed: Server Manger > Tools > DNS
Active Directory Users and Groups are available: Server Manger > Tools > Active Directory Users and Groups
1 – Point to DNS Server
On this new server, we should point DNS server as domain controller, which is also our DNS server.
Find the private IP address of domain controller, using ipconfig command.
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 10.0.0.4
2 – Join Domain
On new server:
Go to: Server Manager > Local Server > Workgroup
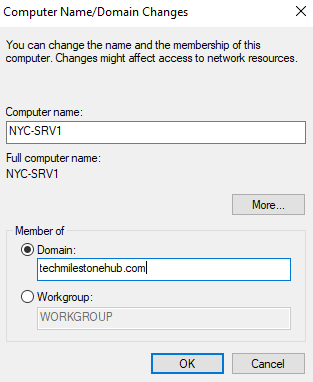
Here put the name of our domain we created using domain controller
It will ask admin credential for domain controller.
Click prompts for restarting.
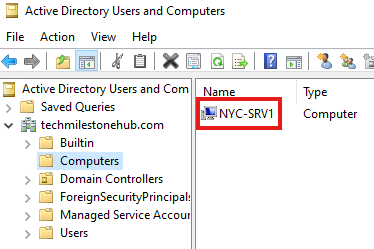
3 – Verify if the new server has joined the domain
In Domain Controller, open tool: Active Directory Users And Groups
Expand Computers, to see the name of new server here
1 – Why we need RODC
Not that often used nowadays.
If on a particular location if there is no IT staffs to manage DC we cannot keep a full DC in that location, because if data gets corrupted, it will be replicated to other DCs.
Also if we don’t keep DC, PCs in that location need to authenticate with DCs in far location which can make it slow, so we ca use a RODC to solve this issue.
RODC can also cache local passwords. If a non-local user like admin tries to login, they can still login through pass-through authentication done by RODC
2 – Deploy RODC
Pre-staging
This is done so that we can ship server to local office and delegate some one to complete the configuration by doing some simple steps.
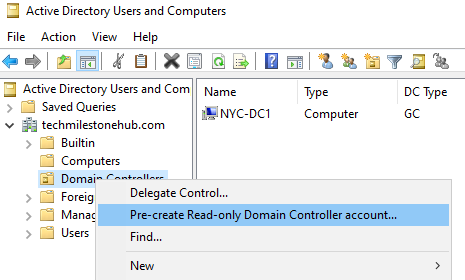
We can create a RODC server blue print in : Active directory Users And Groups, and can assign a group/users to configure RODC in that office
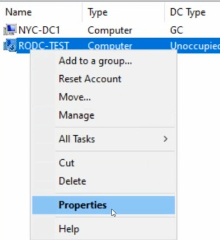
Black down arrow means the server is not physically created yet. We just need to create it.
in properties > password replication policy we can see the account for which it will cache password; the delegated users/groups will be here.
Convert already existing server to RODC
We can also make a server RODC when adding Active Directory Domains And Services Role
1 – Install Active Directory Domain services feature
Do the same steps
2 – Promote to Domain Controller
Same steps
While promoting, select option: Add DC to existing domain

We can deselect DNS
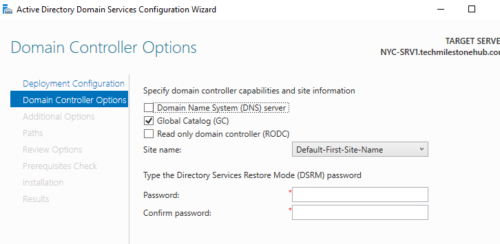
Install from media, if you have a backed up copy of active directory in a USB drive.
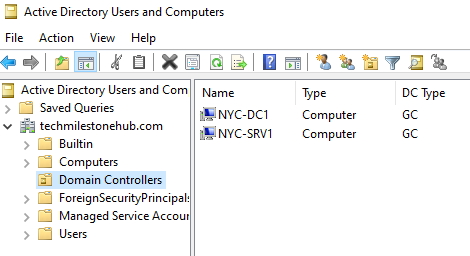
Once added, you will see 2 domain controllers in the Active Directory User and Computers
Windows Remote Manager (WinRM) service must be running to do PowerShell remoting
winrm quickconfig
To check if the server listening to remote connections
To see process running on one server from another, run the powerShell command:
get-process -ComputerName <computer name>
Run a script remotely using PowerShell
Invoke-Command -ComputerName <computer name> -ScriptBlock {<script>}
To connect directly to other server using PowerShell
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <computer name>
exit
PowerShell ISE
Get-Variable, to get all variables present in the memory
To define a variable : $num = 1
To open ISE: ise
Flexible Single Master Operation Roles
There are some jobs in DCs that cannot be replicated to other DCs in domain or it will cause conflicts; There are 5 such jobs; So there are 5 FSMO roles.
2 FSMO roles are forest level roles; Other 3 are domain level roles
Every one of your domain controllers has a read only copy of all five of these roles. So we can recover incase of failure. You can always transfer the role to 1 DC to another, but if you ever want to convert a read only version to the writeable version, that’s called seizing (done if DC dies).
2 FSMO roles are forest level roles;
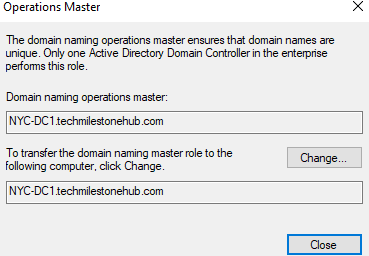
1 – Domain Naming Master
Handles configuration partition of active directory.
It knows about all the trust relationships in the forest.
It also makes sure that all of your domain names are unique.
2 – Schema Master
The schema master is made up of the actual master copy of the schema database.
The schema database is made up of all of the objects and attributes for the entire force.
Every time Active Directory goes to create something, it has to go to the schema to know how to build
whatever it’s going to create.
We will have only 1 writable copy for those 2 roles for entire forest. These 2 roles may be in the root of the forest.
Other 3 are domain level roles
Every domain in forest will get copy of these 3 roles
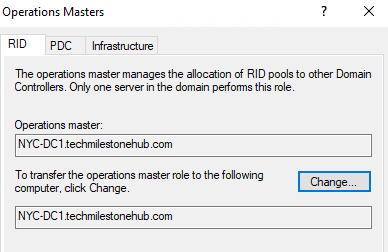
1 – RID Master
Every object in domain has a unique identifier; So every object will get a RID and SID. RID Master handles that.
Does a RID pull out, that is it gives groups of IDs to DCs, so that DCs can use it.
RID master also make sure ID is unique.
2 – Infrastructure Master
The infrastructure master handles what are known as group to user references.
That is, if we want to give group in a sub-domain access to a resource in another sub-domain, it is responsibility of this role.
3 – PDC Emulator Master
Syncs password changes.
Does Time sync:
Now this is important because Active Directory uses a security protocol called Kerberos.
For the sake of Kerberos. Kerberos will only give a five minute leeway period if your machines are out of sync on time.
Handles GPOs
Handles Legacy Authentication
Troubleshooting FISMO Roles
1 – View FSMO roles
Server manager> Tools > Active directory User and computers
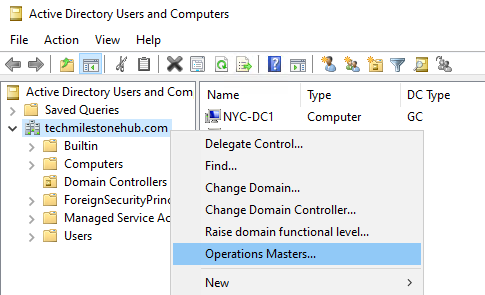
Select Operations Masters
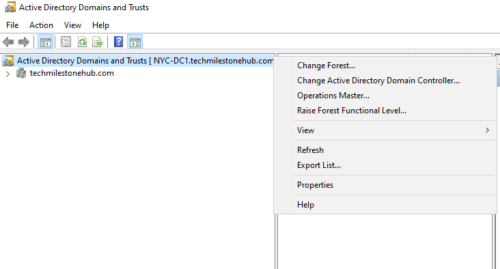
To see Domain Naming Master: Go to Server manager> Tools > Active directory User and computers
Select Operations Masters
We don’t have tools to see schema master; We have to register a DLL file to do it.
Run > regsvr32 schmmgmt.dll
Now go to Microsoft Management Console : Run > mmc.exe
File > Add/Remove Snap-in
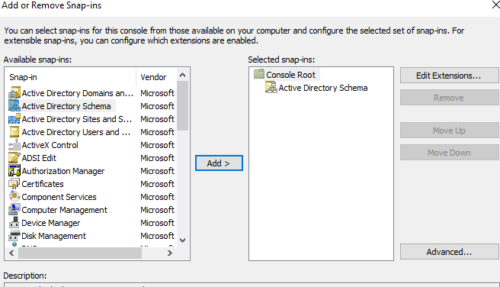
You will be able add Active Directory Schema Tool to Microsoft Management Console now.
Go to operations master
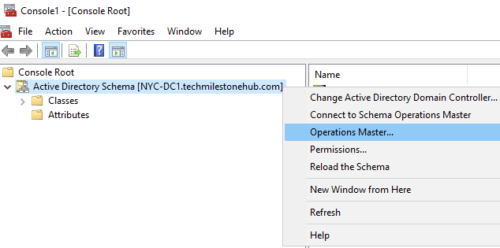
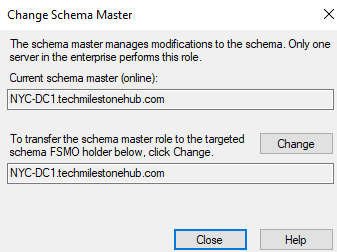
2 – Transfer FSMO roles
When domain controllers are up and running we can do GUI :
Click the change button to change FSMO role to any DCs in the domain
Operations Masters >
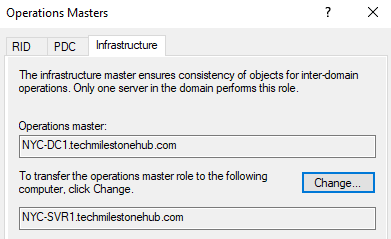
Change will be syncs across all DCs in the domain.
Seizing : When a DC or role is not running
When a DC dies and 1 role is also gone, we need to do seizing. That is to convert a readable copy to a writable copy.
1 – Go to CMD > ntdsutil
NTDS(new technology directory services) was first name of active directory
We have to use this CMD utility to do it.
2 – PoweShell
use command:
Move-ADDirectoryServerOperationMasterRole
There are PowerShell commands for seizing and moving
When a computer in a sub-domain want to access a resource in another sub-domain in another location there need to a 2-way trust, between these sub-domains.
This trust is transitive between all sub-domains. If A trust B and B trust C, then A trust C.
But we cam configure one-directional trust.
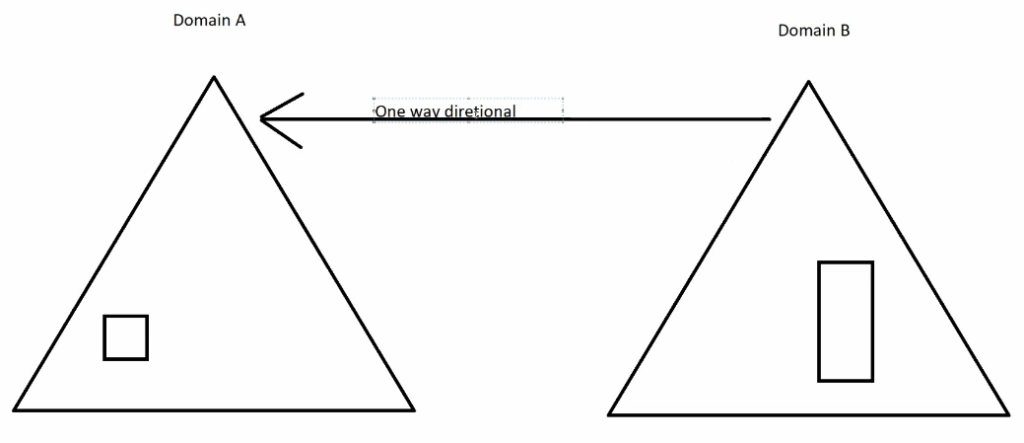
Arrow direction shows direction of trust, not the connection.
Short-Cut Trust: When Transitive trust is slow
When 2 subdomain want to comminute and share source but they have many sub domain in between because they are far away, then they authenticate trough transitive trust through all the sub domains in between them; this make it slow
So to bypass transitive trust we can configure a short-cut trust, so that they can authenticate each other directly.
Realm Trust
To allow resources to be shared with Linux/Unix systems as they are use Kerberos authentication.
Forest Trust
In case of a company merger when 2 main domains need to share resources.
In this case we need to make sure 2 DNS can see each other, for that we nee a WAN or VPN connection between each main domains. We can setup a 2-way or 1-way trust.
Tool: Active Directory Domains And Trusts
Server Manager > Tools > Active Directory Domains And Trusts
There should be some connection between 2 DCs, WAN or VPN. Also, DNS should be able to communicate properly.
Conditional Forwarding
This is done to make DNS of domain A can communicate with DNS of domain B.
To create a conditional forwarding, go to: Server Manager > Tools > DNS
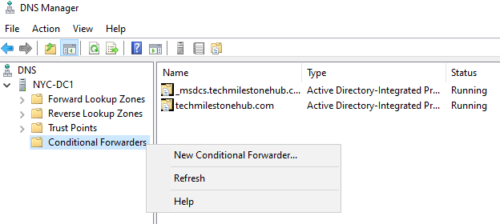
Create a new conditional forwarding:
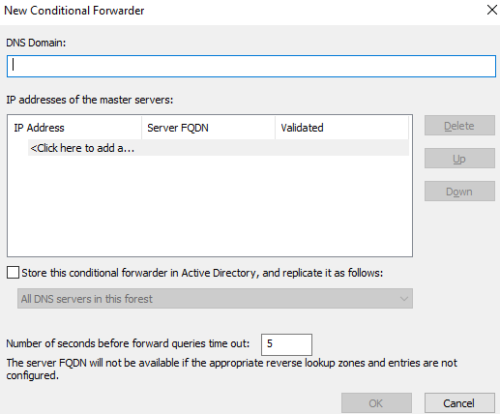
Here put in the domain and IP address of the DNS server of domain B; Do the same in domain B to point to domain A.
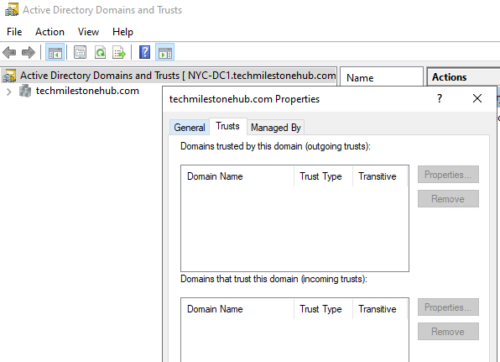
View the trusted domains and domain that trust
Tool: Active Directory Domains And Trusts
Server Manager > Tools > Active Directory Domains And Trusts
right click on domain name > properties > Trusts(tab)
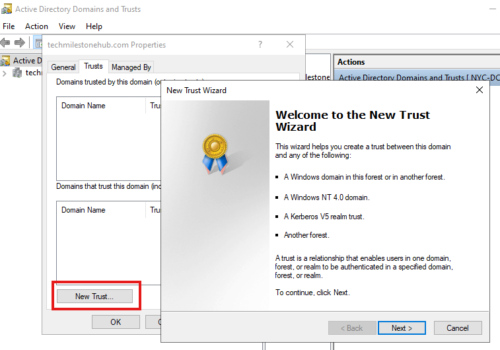
To create a new trust
Server Manager > Tools > Active Directory Domains And Trusts
right click on domain name > properties > Trusts(tab) > New Trust
What is site?
So a site an object in active directory that represents a physical geographical location.
It will help control replication amongst DCs
Sites are linked together using site links or WAN lines
Site can have many domain controllers. Each Domain controller has a component called knowledge consistency checker (KCC).
KCCs on DCs on same site will communicate with each other, and will create a circular replication ring. This is called intra-site replication (with in the site). This ensure users, groups and other object are in sync throughout DCs in the site.
KCCs will also check if all DCs in site are online; If any server goes down it will update the replication ring to include only running servers.
We create site in active directory; Then we move domain controller to correct site.
If different office location have good bandwidth connection, it is ok to have a single site and all DCs to be under 1 site.
Site Links
Site links has name and cost
Faster site link will have lower cost.
Site Link Bridging
Enabled by default in active directory site environment, to make bridge head server communicate. We can alter it so that only few site will only sync every 3 hours and other site can sync independently on their parent site.
If we separate sites, each site will have a Bridgehead Server, which will be responsible for replication within the sites.
Bridgehead Servers of different site will also replicate with each other in every 180 minutes or 3 hours, this is called inter-site replication.
Site Subnets
Sites should have wee defined subnets so that computers with in that subnet will know which domain controller to interact to.
Site Configuration
Do below steps if sites are needed
Go to : Server Manager > Tools > Active Directory Sites And Services
There we will see a default site.
To create new site right click Sites folder > New site
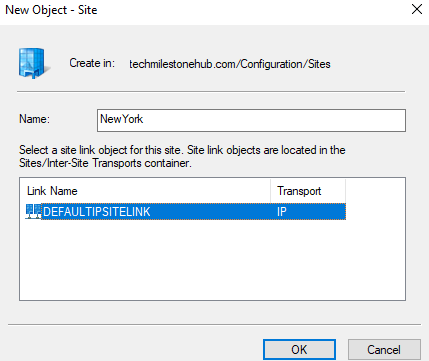
Click Ok
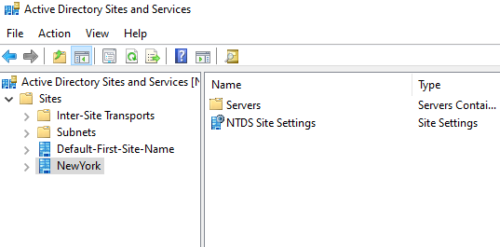
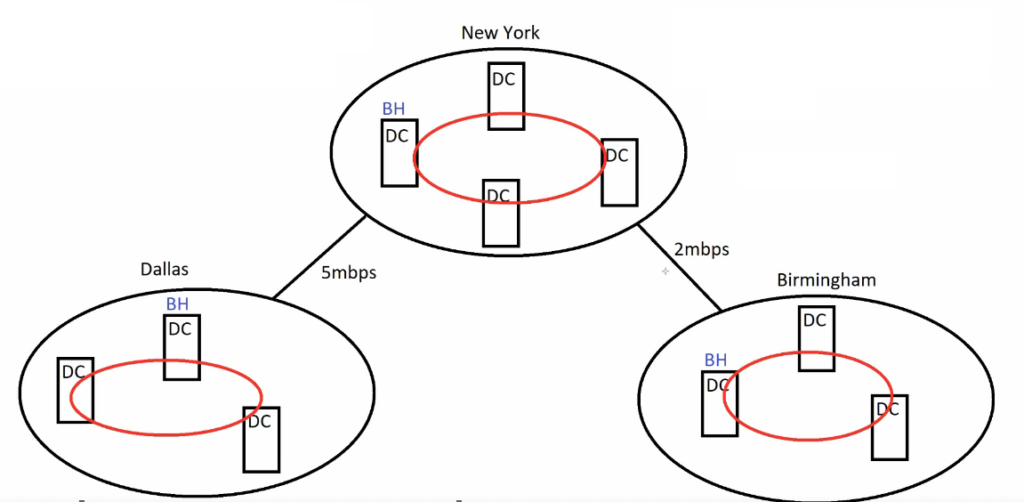
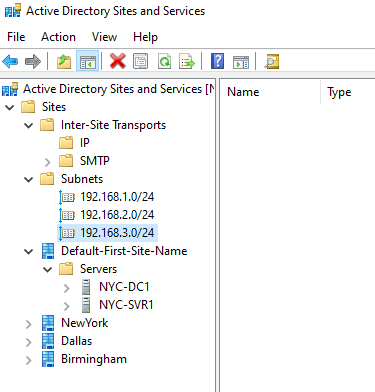
New site will be created; Create 2 more sites (Dallas, Birmingham)like this:
Move Domain Controller To Site
By default domain controller will be in default site.
1 – Create Site Links
We create site links based on our diagram:
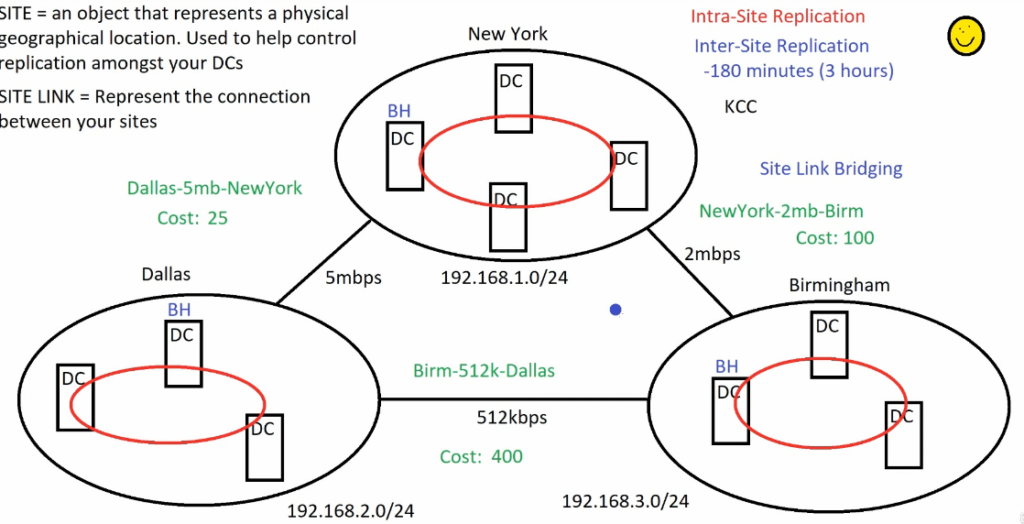
We need to create 3 site link:
- NewYork-2mb-Birm: Connects NewYork and Birmingham
- Dallas-5mb-NewYork: Connects Dallas and NewYork
- Birm-512k-Dallas: Connects Birmingham and Dallas
Go to : Active Directory Sites And Services > Sites > Inter-Site Transports > IP
Here we right click and add new site links.
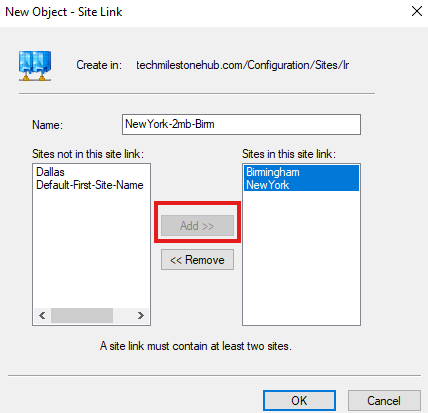
Similarly create all 3 site links
2 – Update site-link cost
Right click on site link > Properties
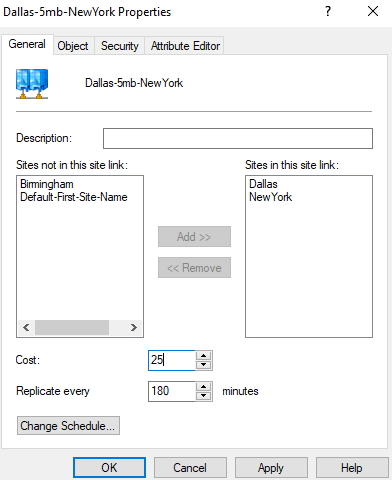
We can update the cost here as per diagram, for all site links.
We can also change replication interval and schedule as well.
3 – Assign Subnets for sites
Right click on subnets to add new subnet.
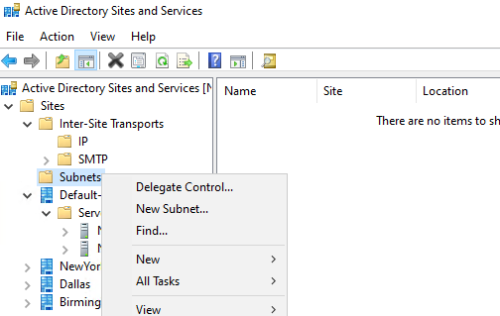
Assign subnet as per the diagram:
- NewYork: 192.168.1.0/24
- Dallas: 192.168.2.0/24
- Birmingham: 192.168.3.0/24
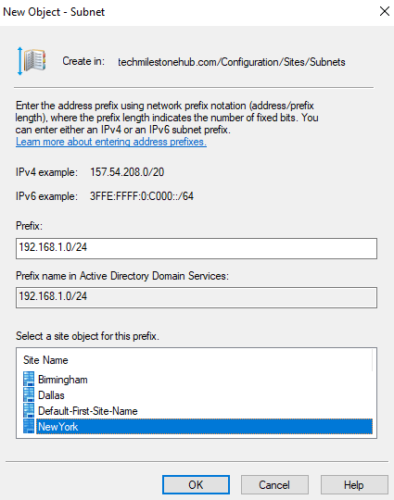
Add subnets for all 3 sites
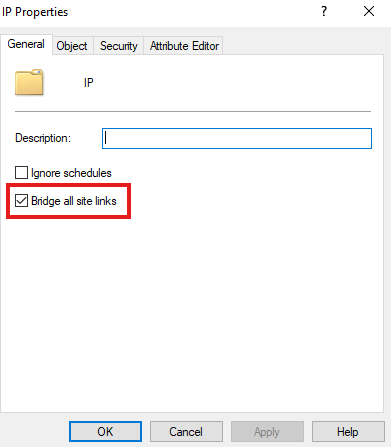
4 – Disable site link bridging and add custom site link bridging (optional)
To disable site link bridging:
Right click IP > Properties
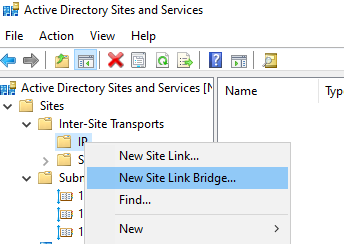
To add custom site link bridge:
Right click IP > New Site Link Bridge
5 – Verify Site information updated in DNS
DNS will be updated instantaneously with site information
Go to : Server Manager > Tools > DNS
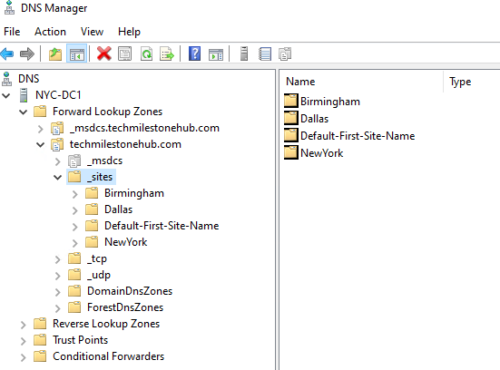
Organizational Units are containers inactive directory to hold user and object like computer;
it can be based con location department etc., based on the company
An object(user, computer etc.) can only be part of a single OU.
We can apply GPO (group policy object), it will be applied to all sub-OUs
With OUs, we can make a user admin of that OU alone.
Folders with book icon are OUs others are called system folders.
Domain Controllers OU is the only OU there will be when first installed.
Create OUs And Users
Right click on domain > New > Organizational Unit
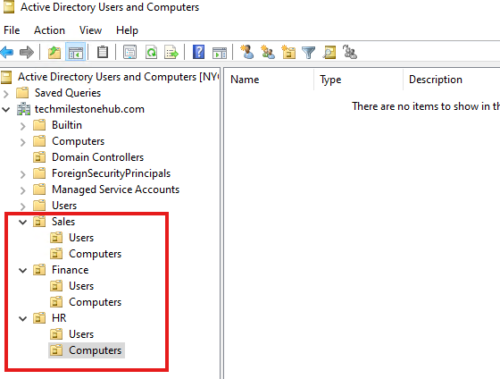
Create sub-OU for computers and groups
Here we are creating OU based on department.
Add user to OU
Right click users OU > New User
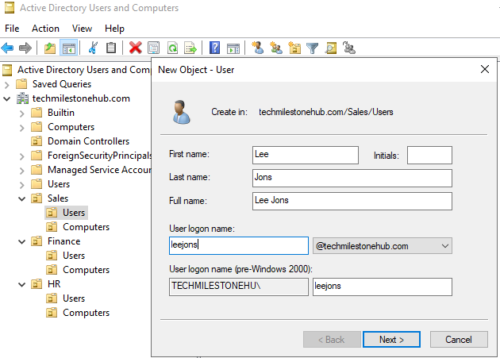
user login name is called user principal name (UPN)
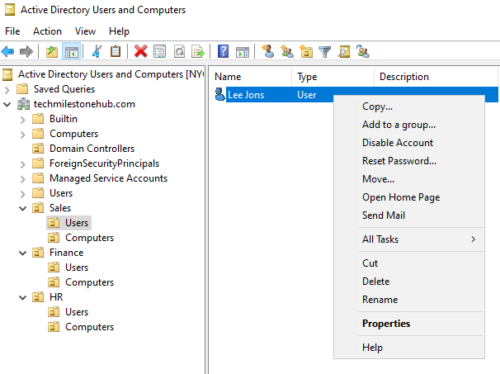
Once user is created we get options to disable, reset, password etc
In properties > Account tab, we can set the log on hours for the user.
Here we can also set the computers to which the user can log on to.
Active Directory Administrative Center
New tool for admins;
Can me made accessible via webpage
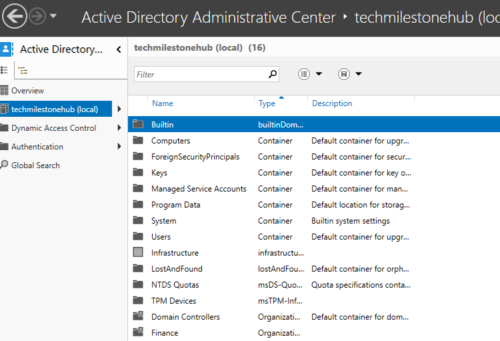
Here also we will be able to see the details and OUs we created
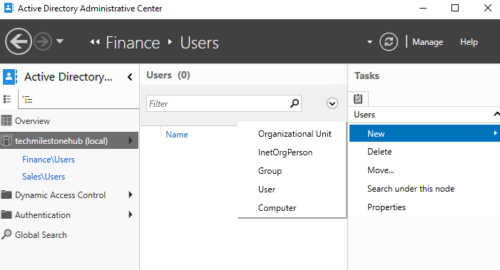
Here also we can create new objects
To delete any OUs
ADUC > View > Advanced features
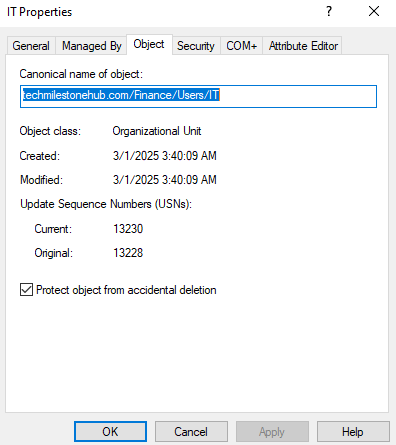
Now if we go to OU properties, we will see more tabs.
Uncheck the protection
Now we will be able to delete it.
Delegate Control To User Over An OU
We will be creating a user in IT OU and will control over sales OU.
Right click OU > Delegate control
click next
Add the user to which we want to delegate control
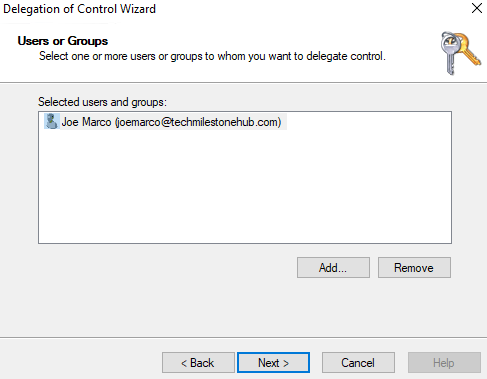
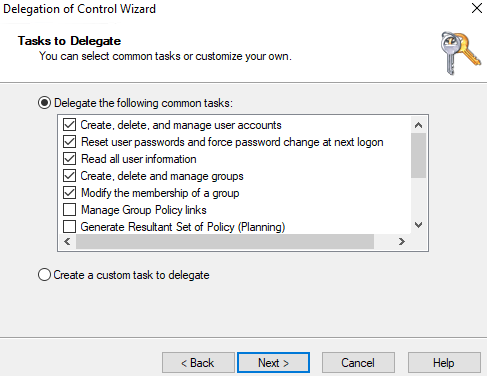
Delegate the tasks
To see what all permission someone has over an OU
Turn on advanced features : View > Advanced features
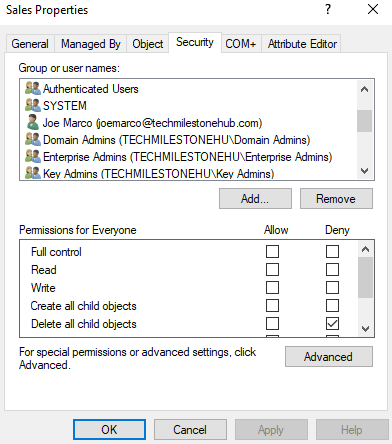
go to OU properties > security tab
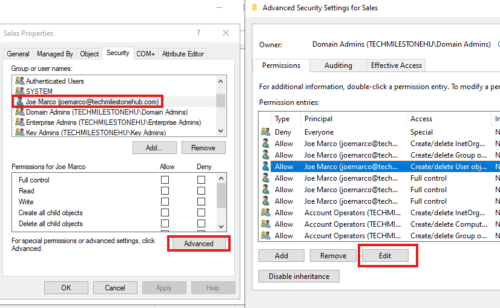
Here we will se lot of permissions to edit.
A group has a type and a scope.
Difference between OU and group is; users can be at multiple groups at a time.
If you delete a group, that will not delete users in a group, unlike OU.
Type
Type can be distribution or security
Distribution Group
Distribution is only for email purposes. If you create a groups with Microsoft Exchange it will be distribution group.
A Distribution group will have a email address, but we cannot give permission to anything
Security Group
We can give permission and will also get an email.
Scope
Group Scope can be:
Global, Domain Local, Universal
Global Groups
Can contain users only from domain they are created, but can be given permissions over other domains.
Domain Local Groups
Every object in active directory has SSID(for identification).
Every resource has ACL(Access control List), ACL contain list of SSID that can access that resource.
To increase performance we need to minimize ACL lookup, so wee need to minimize SSIDs in a ACL of a server. So we use Domain Local group.
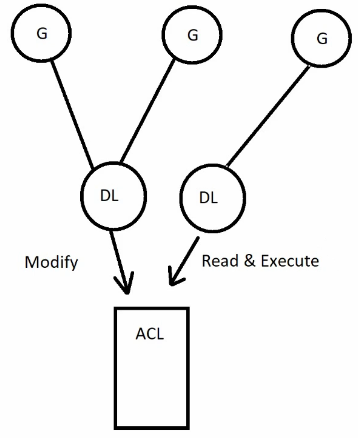
We make other groups member of DL groups to give them necessary permissions.
A>>G>>DL>>P
Accounts go into global groups, global group goes into domain local groups > domain local groups are given permissions.
Universal Groups
Groups in different domain can be member of this universal group, so that they can access resource in a particular domain.
For example, sales departments of all domains can be part of universal sales group, so that they can access a server in a particular domain.
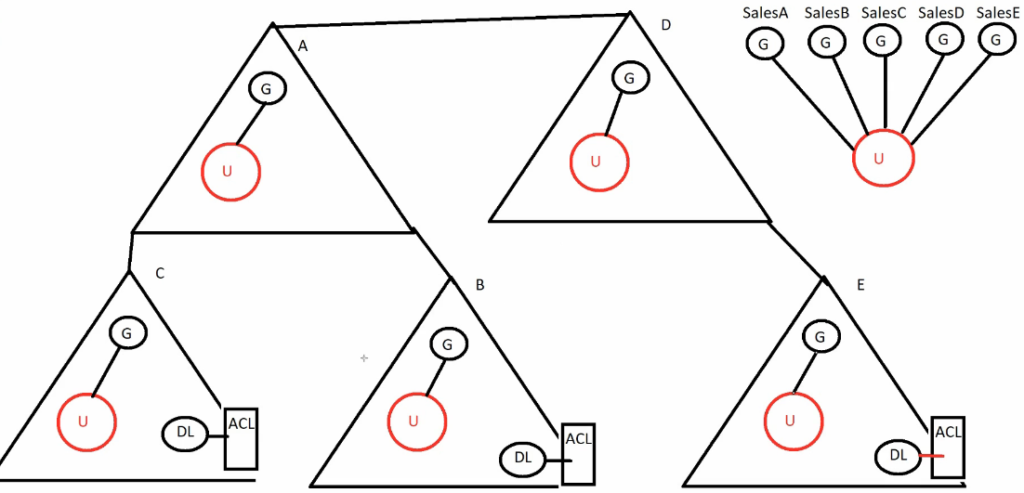
universal group when created will have a copy in all domains; Admin of that domain is responsible for adding sales group of that domain to universal sales group. Now all sales user will be in the universal group.
A disadvantage of universal group is that, it will take up some replication traffic to various domains.
Create And Manage Groups in Active Directory
In Users, Built-in folders we can see some existing groups
Enterprise admins is the most powerful group in active directory. They have admin right over all domains that are part of the forest.
Domain Admin can only manage that domain.
Schema Admins can change schema of active directory.
Create Groups
Right click on any OU to create new group
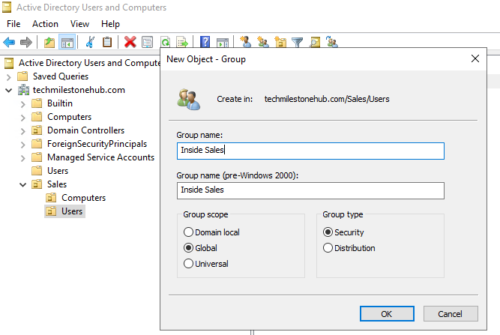
Create 3 sales groups in sales OU
If all sales groups want to modify a resource in the domain, instead of giving each group permission over that resource, we create a domain local group. And link different groups in to that.
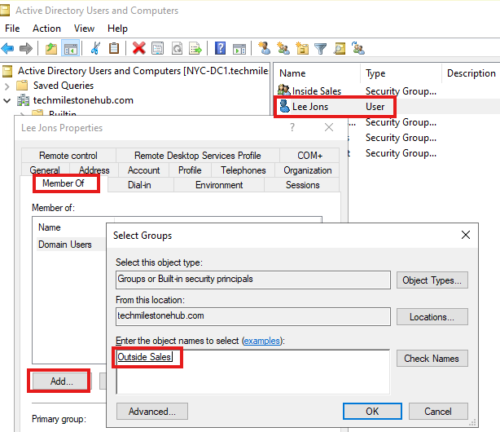
Adding A User and groups to a Group
Right click on user and go to user properties, then in member of tab, you can add the group for the user
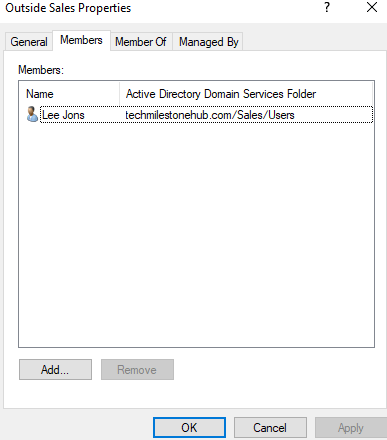
We can also add user using members tab in group properties:
Similarly add sales group to domain local groups:
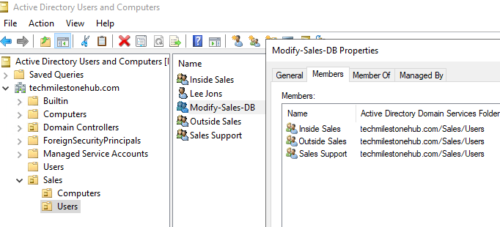
On a domain resource, like a folder, we give permission to the domain local group, not the individual groups.
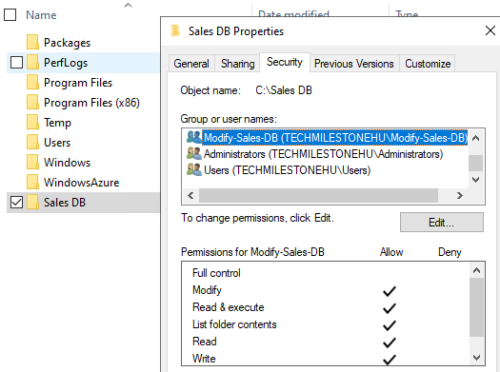
Here we are giving modify permission to DL group over Sales DB folder. So here we have only 1 ACL entry for all 3 groups.
Special Groups
To see special groups we need to go to ACL.
Click Advanced > Find Now
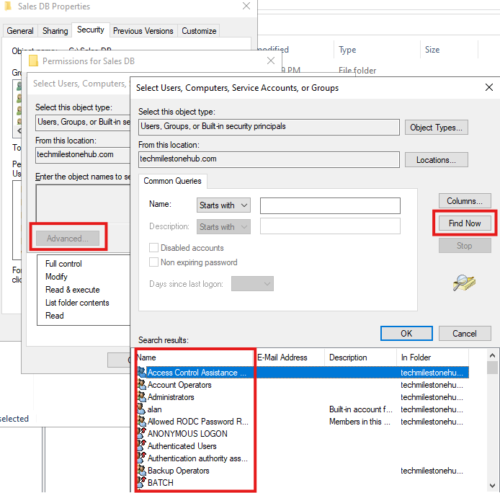
Here there special group the we don’t modify:
Authenticated Users, Interactive(User logged on locally to the machine), Network(User in the network), Everyone
We can give permissions to these groups to access resources.
Universal Group Membership Caching
UG get replicated with Global Catalog Servers only, so they can be managed by GC servers only.
GC servers has a list called Universal Group List
When user logs in DC checks with GC server if the user is in UGL.
So if GC server is in another site that can cause delay
Option 1 :
We can make that DC a GC server, but it will cause replication, and will consume replication bandwidth
Option 2:
Feature by Microsoft : Universal Group Membership Caching (UGMC)
If we enable UGMC in a site, DC in that site will cache(read-only) UGL on that DC
To turn it on:
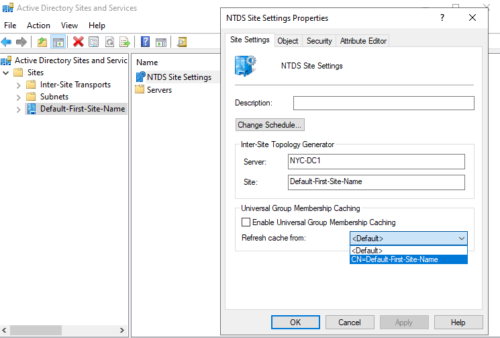
Go to NTDS site settings properties. Here you can also choose the GC server to cache from.
Create New OU using PowerShell
Get-Command -Noun *org*
This will get all commands with org in it.
These are some account used by services that are running in the server, they are managed by active directory itself, so their password are changed by active directory itself.
We have to use PowerShell for that.
1 – Add-KdsRootKey
Add-KdsRootKey -EffectiveTime ((Get-Date).AddHours(-10))
2 – Create Service Account
New-ADServiceAccount -Name TestGMSA -DNSHostName testgmsa.techmilestonehub.com -PrincipalsAllowedToDelegateToAccount “Domain computers”
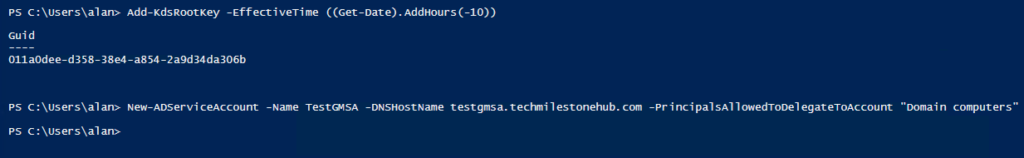
Any computer in the group “Domain computers” will have the right to link on that account, and use this account for services.
If we want to extend it to other computers:
Install-ADServiceAccount -Identity testgmsa
To have the necessary active directory command installed:
Add-WindowsFeature rsat-ad-powershell
Import-Module activedirectory
3 – Link The New Service Account with the service
Go to properties of service and in log on tab, browser for the service account we created.
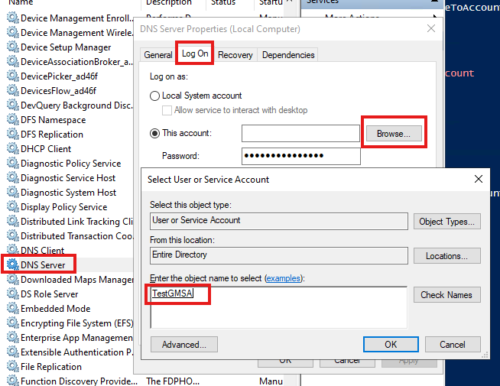
Leave the password blank
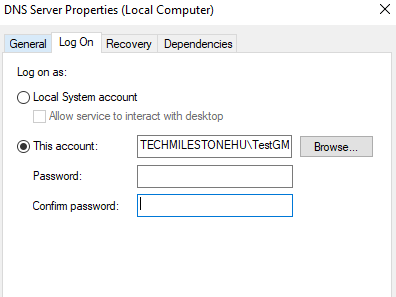
AD will se the password.
We can use VPN gateway or express route to connect on premise to Azure DC
While creating Microsoft Entra Domain Services in azure virtual network should be different from on premise.
